According to many experts, chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease caused by infection of possible connection of autoimmune disorders, which is characterized by damage to the organ parenhimal and interstitial tissue.The disease has been familiar with medicine since 1850, but today it is still not well -studied and poorly treated.Chronic bacteria (6 - 10%) and non -bacteria (80-90%) prostatitis are the most common and socially significant inflammatory diseases in men, which significantly reduce their quality of life.The disease is mainly recorded in young and middle -aged people and is often complicated by impaired copulations and generational functions (reduction of efficiency, infertility, etc.).The disease is registered for men in 8-35% of cases aged 20-40.
The cause of bacterial prostatitis is a pyogenic plant that penetrates the iron from the urethra, or from lymphogen and hematogenic paths.Ethiology and pathogenesis of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis.Mostly men over 50 are suffering.
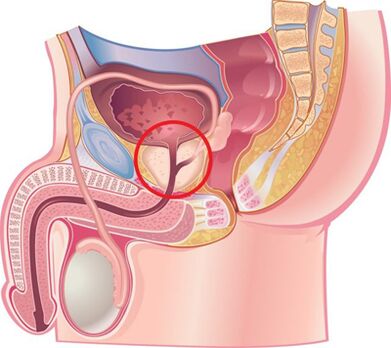
Causes of the development of the disease
Chronic prostatitis is currently considered to be a polyetiological disease.There is a opinion that the disease occurs as a result of penetration of infection into the prostate and then continues without the participation of the pathological process.This is facilitated by many non -infectious factors.
Infectious factors in the formation of chronic prostatitis
In 90% of cases, pathogens enter the urethra, resulting in acute or chronic prostatitis.There were cases of asymptomatic car.The course of the disease is influenced by the condition of the human body and the biological properties of the pathogen.It is assumed that the transition between acute and chronic prostatitis occurs due to the loss of elasticity of fibers due to excessive production of fibrous tissue.
The following pathogens can be found between chronic prostatitis causal agents:
- In 90% of the cases, the disease discovers Gram -negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), enterococcus faecalis (stool enterococcus), and slightly less frequently -pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp.Acinetobacter spp.Gram-positive bacteria are rare for enterorococci, streptococci and staphylococci.
- The role of koagulase-negative staphylococci, ureaplasma, chlamydia, trichomonas, garderella, anaerobic bacteria and the Candid genus were not fully clarified.
The infection enters the prostate in several ways:
- The increasing path is most likely, as confirmed by a common combination of prostatitis and urethra.
- Hematogenic prostatitis develops when the infection penetrates the gland in the bloodstream, which is in chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, periodontitis, pneumonia, cholecystitis and collangitis, turmoil, etc.
- Contonent chronic prostatitis develops with urethra and urethral strikes when the infection penetrates the gland that is growing with urinary flow, the purulent infections of the kidneys, epipiditis, defentition and function canalicularis, diagnostic and therapeutic urological manipulations (cat.also.
- Lymphogenic infection penetrates into the prostate with procts, thromboflebitis of hemorrhoids, etc.
Non -contagious factors in the formation of chronic prostatitis
Chemical factors
According to experts, the leading role of chronic prostatitis is associated with intraprostatic reflux urine when urine is poured from the urethra into iron, leading to a violation of the evacuation of prostate and talked vesicles.
In the case1- Adrenoreceptors cause dynamic obstruction and contribute to the formation of new intraphostatic refluxs.
The urates in the urine, with refluxs, lead to the formation of a "chemical inflammatory reaction".
Hemodynamic disorders
Support chronic inflammation of the circulatory disorders in the pelvic organs and scrotum.Stagnation develops in people leading sedentary lifestyles, such as drivers, office employees, etc.Person, obesity, sexual withdrawal, sexual sexual dysmetry, frequent hypothermia, mental and physical overloads.Maintaining the inflammatory process, spicy and spicy foods, alcohol and smoking, etc.
Other factors
Many other factors support the chronic inflammatory process in the prostate.They belong to:
- Hormonal.
- Biochemical.
- Violation of the immune response.
- Autoimmune mechanisms.
- Infectious and allergic processes.
- The characteristics of the structure of the prostate glands, which leads to the difficulty of total drainage.
The causes of chronic prostatitis can often not be determined.
Classification of prostatitis
According to the United States National Institute of Health, proposed in 1995, prostatitis is divided:
- Sharp (category I).5-10%.
- Chronic bacterial (category II).6-10%.
- Chronic non -bacterial inflammation (category IIia).80 - 90%.
- Chronic non -bacterium is non -inflammatory (category IIIB) or chronic pelvic pain.
- In an accident chronic prostatitis (Category IV).
Signs and symptoms of chronic prostatitis
The process of chronic prostatitis is long but not monotonous.Aggravation periods are replaced by relative lull periods, which occur after a comprehensive anti -inflammatory and antibacterial treatment.
The formation of chronic bacterial prostatitis is often preceded by the nature of the bacteria or gonorrhea, non -bacterial circulatory disorders in the pelvic organs and scrotum (hemorrhoids, varicocells, etc.).
Patients with chronic prostatitis present many complaints.Doctors have been treated for years, but they are very rarely examined for prostate disease.About a quarter of the patients do not submit a complaint or the disease has small clinical symptoms.
Patients with chronic prostatitis can be conditionally divided into several groups.
Urine disorders associated with the narrowing of the urethra:
- Difficulties at the beginning of urination.
- A weak flow of urine.
- Periodic or urination has fallen.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Symptoms caused by irritation of nerve endings:
- Frequent urination.
- Calls for urination are sharp and strong.
- Watering in small portions.
- Incontinence of urine during the desire for urination.
Pain syndrome:
- The intensity and nature of pain vary.
- Localization of pain: lower abdomen, perineum, rectum, groin and lower back, inner thighs.
Sexual dysfunction:
- Pain in the rectum and urethra during ejaculation.
- Slow erection.
- Loss of orgasm.
- Early ejaculation, etc.
From the nervous system: neurotic disorders in the form of fixing the attention of patients to their health.
Signs and symptoms of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis
Chronic Pool Pain Syndrome (CPPS) occurs with the usual symptoms of chronic prostatitis, but there is no bacterium in the third part of the urine and in the secretion of prostate.Chronic non-bacterial interstitial cystitis, rectal diseases, pelvic floor spastic syndrome and functional prostate lesions, which can be caused by organ innervation and hemodynamics, can be simulated by CPPs.
If the Neuroveggetive function deteriorates, the interruption of the innervation of the atony and the gland can be observed, which is shown by the difficulty of closing the urethra lumen.In this case, after urination, urine continues to be released as a drop for a long time.In such patients, the study shows instability and increased irritability, which is shown by increased sweating and irritability of heart activity and changes in dermographer.
The complications of the disease
Chronic prostatitis is complicated by the complexity of sexual and reproductive disorders such as vesiculite and epipidimitis and organ sclerosis.The sclerosis of the organ worsens local microcirculation and uodynamics and the results of surgical interventions.Fibrosis of perihumetral tissues leads to the formation of urinary disorders.
Diagnosis
Due to the fact that there are many causes of chronic prostatitis, the entire complex of diagnostic tests is used to diagnose it.The success of treatment depends on the correct determination of the causes of the disease.Diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is based on the following data:
- Classic symptoms.
- A complex of physical methods (rectal examination of the prostate finger).
- A complex of laboratory methods (urinary analysis of prostate and microscopy, microflora sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, general urine and blood analysis).
- Gonococoos, bacterioscopy smear for urethral, PCR and serological methods (detection of fingertips and chlamydia).
- Urofluometry.
- Prostate biopsy.
- Complex of instrumental methods (ultrasound).
- Determination of the patient's immune system.
- Determination of the neurological state.
- With the efficiency of the treatment and the development of complications, calculated and magnetic resonance imaging, blood sowing, etc.
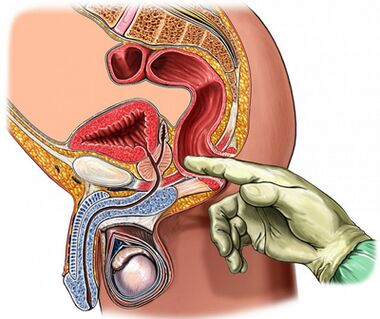
The palpation of the prostate gland
The palpation of the prostate, which is reduced during the aggravation and during the inflammatory subsidiary period, is extremely important in diagnosing the disease.In chronic prostatitis, it is swollen and painful during the aggravation of iron.
The density of organ consistance may be different: the softening and compression areas are palpated and the western zones are determined.When palpation, you can evaluate the shape of the gland, the condition of the seeds and the surrounding tissues.
The process of transrectal finger tests is combined with the seizure of the gland.Occasionally you need a secret from each stock separately.
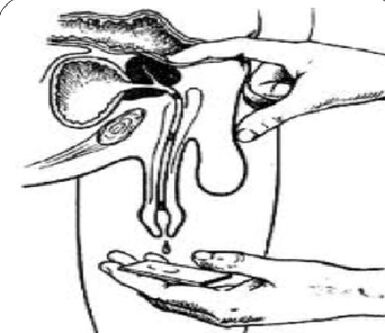
3 glasses of urine and the secret of the prostate
Golden standard for diagnosing chronic prostatitis:
- A collection of the first part of the urine.
- Collection of the second part of the urine.
- To obtain the secrets of the gland by massage.
- A collection of the third part of urine.
Microscopic and bacteriological examination of the substance is then performed.
With inflammation of the prostate:
- The microbial number (CFU) exceeds 103/ml (104/ml for epidermal staphylococci), but should not be neglected with a few dozen and hundreds of microbes.
- The presence of 10-15 leukocytes in the field of vision with the microscope is a generally accepted criterion for the presence of the inflammatory process.
The secret of the prostate and the third part of the urine are subjected to microscopic and bacteriological examinations:
- In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the number of leukocytes is released in the secret of the gland and in the third part of the third massive part of the urine, and the bacteria (mainly intestinal group) are released.
- In the case of non -bacterial prostatitis, the number of leukocytes is observed in the secret of the gland, but the microflora is not observed.
- CTB does not have increased amounts of white blood cells and microflora.
Normal indicator of the secret of the prostate:
- LEUKOCITY in the field of view is less than 10.
- Lecithin particles are large.
- No microflora.
It can be found in the chronic prostatitis of the prostate secrets:
- The number of leukocytes in the field of view is 10-15 over.
- The amount of lecithin particles is reduced.
- The pH of secretion is shifted to the alkaline side.
- The content of acid phosphatase decreases.
- Liszyme activity increases.
Achieving the negative results of the prostate secret once does not prove the lack of an inflammatory process.
The value of testing the prostate secret remains.Usually during crystallization, they form a characteristic pattern in the form of fern plates.In the event of a violation of the aggregation properties of the prostate secret, such a pattern does not constitute what is done with changes in the androgenic hormonal background.
Ultrasound
In case of suspected prostate disease, ultrasound examination of the gland itself (temporary ultrasound), the kidneys and bladder, which allows the following:
- The volume and size of the gland.
- The presence of calculus.
- Size of seed bubbles.
- The condition of the bladder walls.
- The amount of the remaining urine.
- Clothing structures.
- Another type of pathology.
Other prostate research methods
- The state of uodynamics (studying urine flow rate) can be easily and easily determined by using a study such as Uroflowetry.The study can help detect the signs of infravitic obstruction in time and to perform dynamic observation.
- Punctual biopsy is performed with suspicion of abscess, benign hyperplasia and prostate cancer.
- Radiological and endoscopic examination is performed to clarify the causes of infravidular obstruction.
- It is recommended to carry out the urethra examination with a long -flowing inflammatory procedure.
Differential diagnosis
Chronic prostatitis should be distinguished from vesiculoprostatostasis, vegetative prostatopathy, congestive prostatitis, bladder neck, urethral, tuberculosis, tuberculosis, prostate and bladder cancer, urolithiasis, chronic epipidimitis, hypoin.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis should begin with a change in the patient's lifestyle and diet.
Medicines affecting different parts of the pathogenesis are used simultaneously when treating the disease.
The main directions of therapy:
- Eliminate causal microorganisms.
- Anti -inflammatory treatment.
- Normalization of blood circulation in the prostate and pelvic organs.
- Normalization of proper drainage of prostate acini.
- Normalization of the hormonal profile.
- Prevention of organ -sklerosis.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat chronic prostatitis:
- Antibacterial.
- Anticholinerg.
- Tangents.
- Alpha1- ADRENERG blockers.
- 5 alpha -reductase inhibitors.
- Cytokine inhibitors.
- No -steroid anti -inflammation.
- Angioprotectors.
- Immunomodulators.
- Preparations affecting the replacement of the urates.
Antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis
Antibacterial therapy should be performed, taking into account the sensitivity of the microorganisms detected in antibiotics.Empirical antimicrobial treatment is used in the case of non -detection of the pathogen.
The drugs chosen are the fluoroquinolones of Generation II - IV.They rapidly penetrate the glandular tissues with normal use methods, showing activity against a large group of Gram -negative microorganisms and ureaplasma and chlamydia.In case of failure of antimicrobial treatment, it should be assumed:
- Microflora polyurezance,
- Short (less than 4 weeks) treatment courses,
- Incorrect selection and dose of the antibiotic,
- Changes in the type of pathogen,
- The presence of bacteria living on the prostate channels, covered with protective extracellular membrane.
The duration of treatment should be at least 4 weeks with the mandatory later bacteriological control.In case of preservation in the third part of the urine and the secret of the bacteriuria prostate more than 103Re -antibacterial therapy is prescribed for 2-4 weeks.
Cytokine inhibitors in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Cytokines are glycoproteins selected by immune and other cells under inflammatory and immune response conditions.They are actively involved in developing the chronic inflammatory process.
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs have an anti -inflammatory effect and reduce pain and fever.It is widely used to treat chronic prostatitis in the form of tablets and cones.The most effective way to submit is the rectum.
Immunotherapy
In addition to antibiotics and anti -inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators are used in the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis.The most effective is the administration of the rectal path.An immunomodulator is widely used, increasing the functional activity of phagocytes, which contributes to the more effective elimination of pathogens.
Alpha blockers in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
It has been found that alpha-1 adrenergic blockers normalize the sound of the prostate urethra, seminal vesicles and prostate capsules, which in this group treats drugs very effectively in the treatment of the disease.Alfa-1 adrenergic blockers are used in patients with severe urination disorders in the absence of an active inflammatory process.
For CPPs, the treatment period ranges from 1-6 months.
5a reductase inhibitor in the treatment of abacterial prostatitis and
It has been found that the 5A reductase enzyme has resulted in testosterone 5A-dihydotrotestosterone prostate form, which is more than five times higher than testosterone activity, which leads to an increase in epithelial and stromal components in the elderly.
If you take the inhibitor of 5A reductase for 3 months, the atrophy of the stroma tissue for 6 months is inhibited by the secretory function, the decrease in the severity of the pain and the glandular volume, the tension of the organ and the edema.
The role of anti -clerotic drugs in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
In the prostate gland, the fibrosis develops in the case of long -flowing inflammation, which is indicated by microcirculation and uodynamic disorders.Anti -clerotic drugs are used to prevent the fiber.
Other medicines used to treat chronic prostatitis
Together with the above drugs, the disease is used to treat the disease:
- Antihistamines.
- Vasoders and angioprotectors.
- Immunosuppressors.
- Preparations that affect the replacement of the urates and the trinodic salt of the citric acid.
Vegetable products
It is effective in treating prostatitis in the form of suppositories containing a complex of biologically active peptides isolated from the prostate gland of cattle.
It occurs as a result of the drug:
- Stimulation of metabolic processes in the tissues of the gland.
- Improving microcirculation.
- Reducing swelling, leukocyte infiltration, stagnation of secretions and pain.
- Preventing thrombus formation in prostate venulas.
- Increased activity of Acini's secretory epithelium.
- Improving sexual function (increasing libido, restoring erection function and normalizing spermatogenesis).
The prostate massage is a finger massage
Many researchers claim that chronic prostatitis should be used finger massage, taking into account the known contraindications.
Physiotherapy
The efficiency of physiotherapy procedures in the treatment of prostatitis has not been proven today, the mechanism of action was not scientifically known and the side effects have not been studied.
To prevent chronic prostatitis
When you start preventing the development of chronic prostatitis, you should know:
- The risk of developing the disease increases with age.
- Representatives of the Negroid species tend to the disease.
- Family willingness to illness cannot be excluded.
People who tend to develop chronic prostatitis should be more attentive to their health.
Disease Prevention Tips:
- Take sufficient amounts of liquid.Frequent urination promotes leaching from the urethra.
- To prevent diarrhea and constipation.
- Follow the rational diet.Do not eat foods with carbohydrates and saturated fats that lead to an increase in body weight.
- This should be limited to the use of the urethral irritation materials: sharp and spicy foods, smoked meats, sauce and spices, coffee and alcohol.
- Refuses to smoke.Nicotine negatively affects the condition of vascular walls.
- Do not cool up.
- Do not keep the bladder emptying.
- Lead an active lifestyle, exercise.Perform the exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles, which allows you to eliminate the stagnation of venous blood, which in turn supports the normal function of the prostate gland.
- Lead regular sex life.Avoid prolonged abstinence.Iron should get rid of the secret in time.
- Stay followers of monogamous relationships.Illegal sexual relationships increase the likelihood of acquiring sexually transmitted diseases.
- If complaints appear by the urogenitin authorities, contact the urologist immediately.